Take MySQL Database Backup From Jenkins
In this post, we will explain and practically show how you can configure MySQL database backup using Jenkins jobs. in easy words, you will automate the MySQL database backup process from Jenkins GUI and MySQL dump command. Normally we use MySQL dump from CLI or using the windows option. In this case, just automate the MySQL dump triggering from a shell script which will be called by Jenkins job with parameter. MySQL dump needs few parameters to run just pass them by build with parameter option in jenkins.
1. Log to Jenkins default URL and port: http://192.168.56.21:8080/
If you want to install and setup Jenkins see this article
2. Go to New items
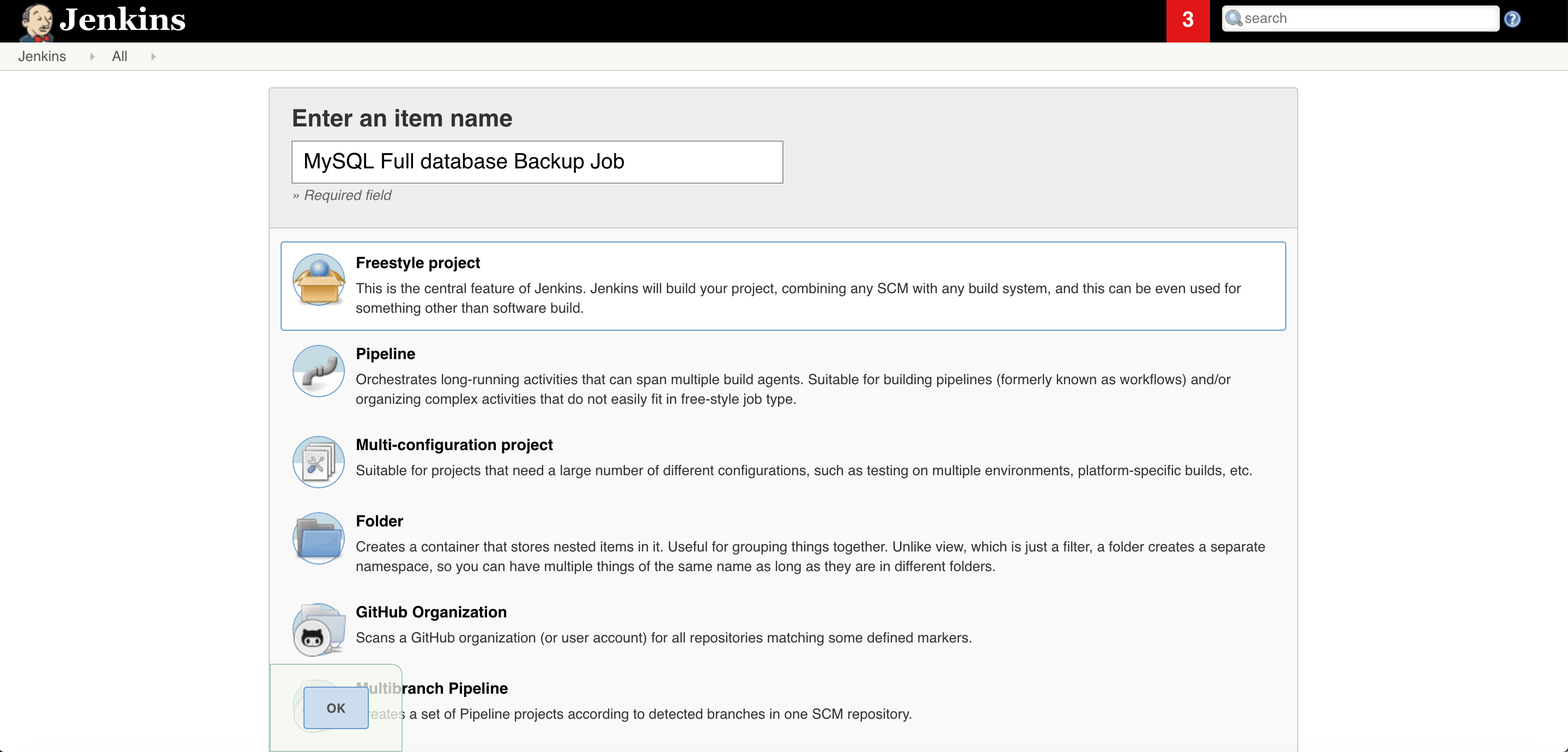
3. Give some Name and select FreeStyle project
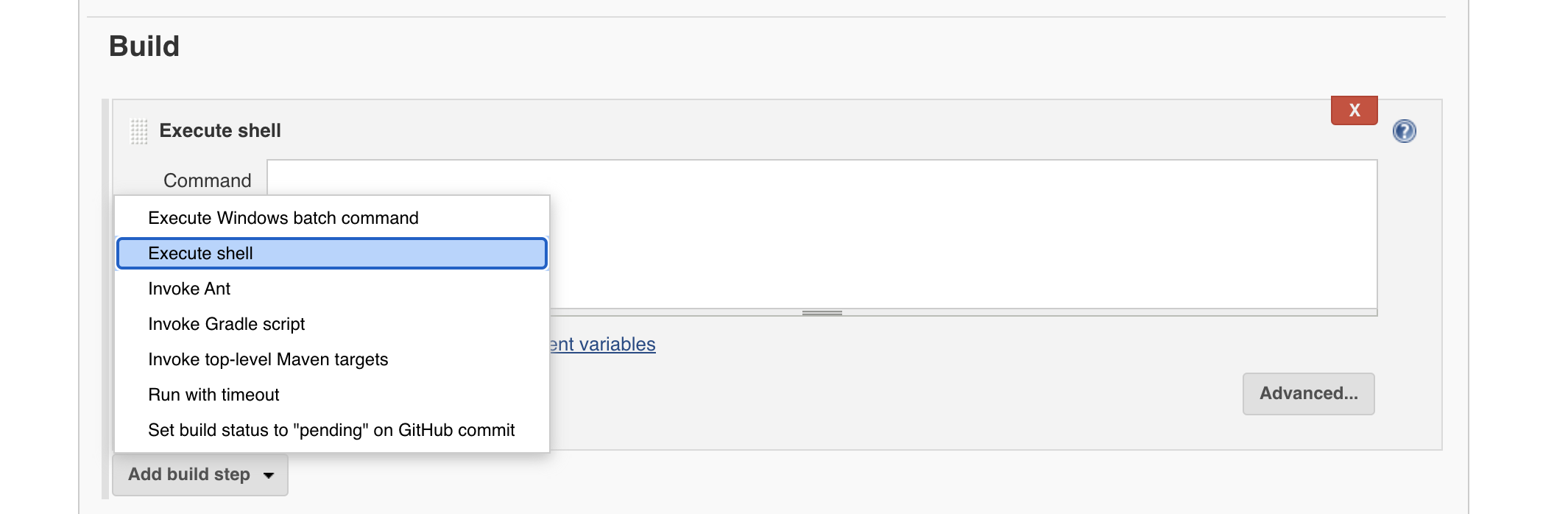
4. In the build section click on Add build step radio button and select Execute shell.
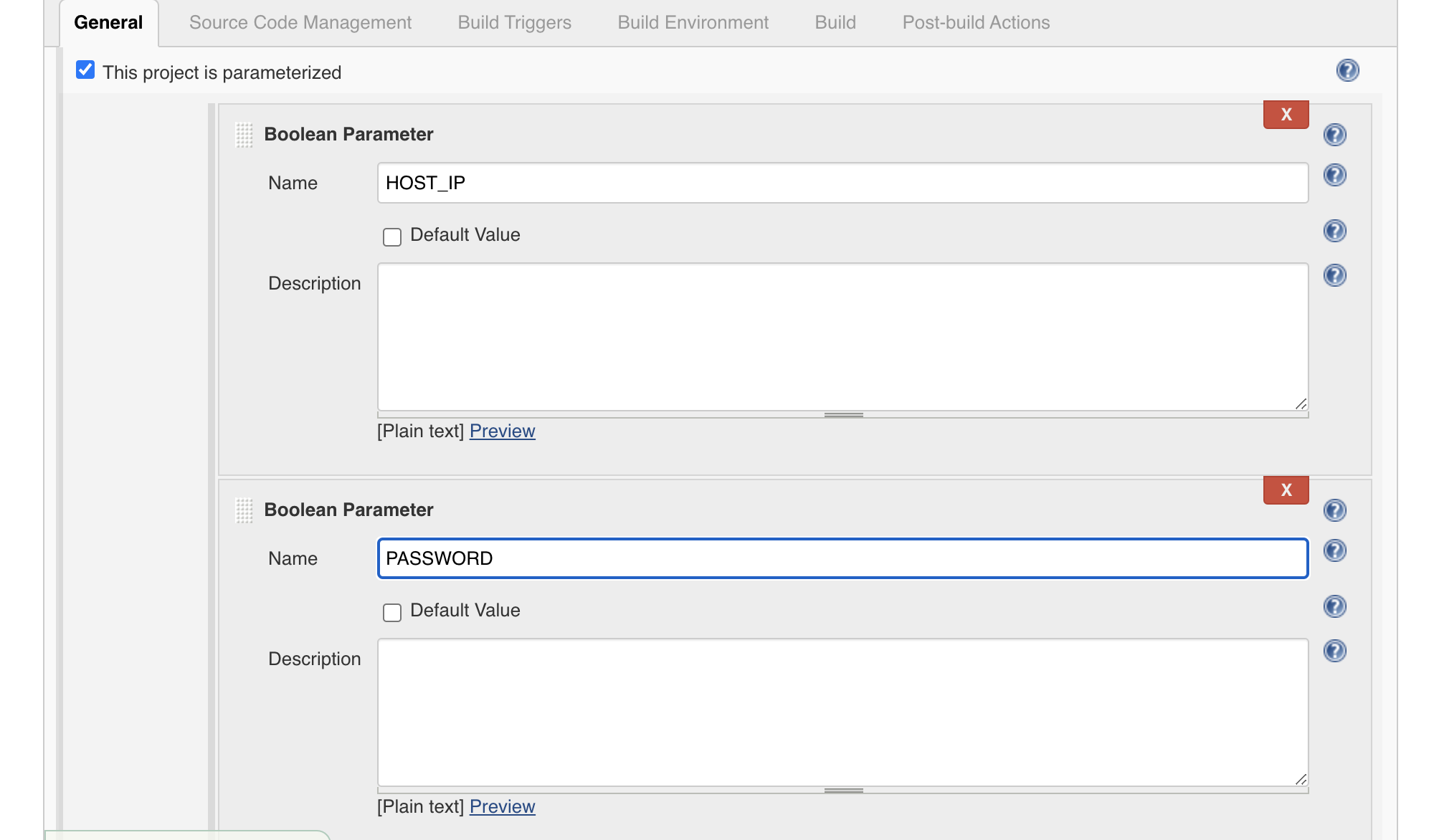
5. Select boolean parameter for MySQL database host and database superuser password which is root password in MySQL database case.
6. In this build part give the shell script name with full path and parameters like $HOST_IP & $Password
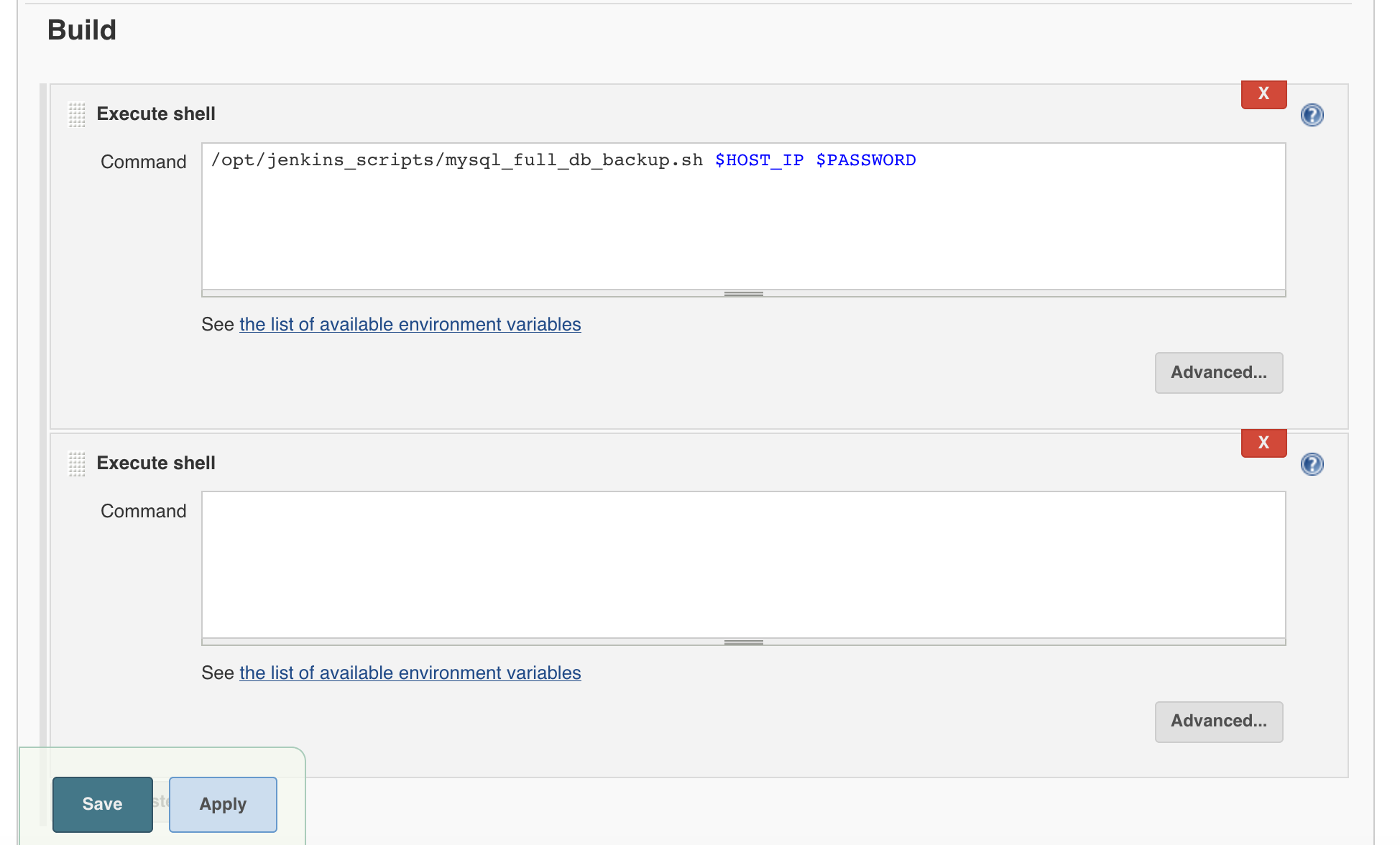
Shell Script
[root@master01 ~]# cat /opt/jenkins_scripts/mysql_full_db_backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
HOST_IP=$1
PASSWORD=$2
echo "starting mysql database full backup"
mysqldump -h $HOST_IP --all-databases --single-transaction --quick --lock-tables=false > /opt/jenkins_scripts/mysql_backup/full_backup_$(date +%F_%N).sql -u root -p$PASSWORD
echo "Backup has been done"
[su_box title=”IMP Note” box_color=”#fe2227″ title_color=”#101112″]Note: Make sure Jenkins have execute (chmod +x /opt/jenkins_scripts/mysql_full_db_backup.sh) privilege on script[/su_box]
7. Let’s execute the Jenkins job
7.1 click on the the MySQL database backup job
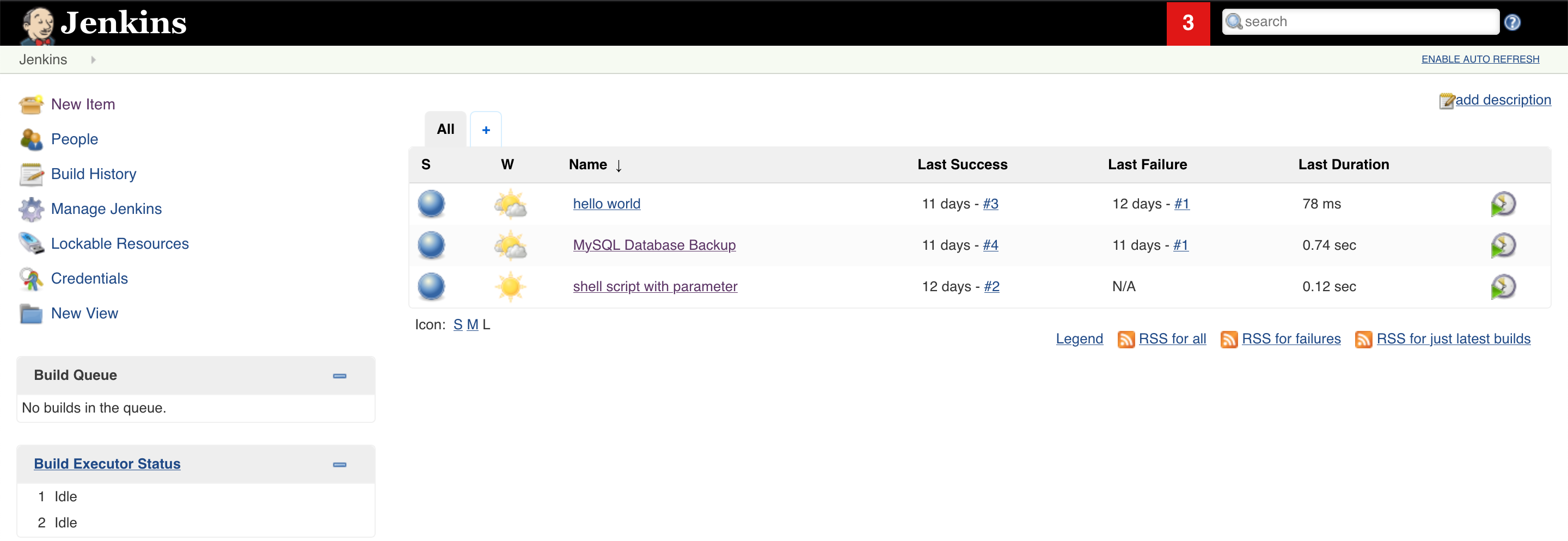
7.2 Click on build with Parameter
7.3 Give your database server name or IP. In my case Mysql database running on the same server that’s thy, I will give localhost and database root password
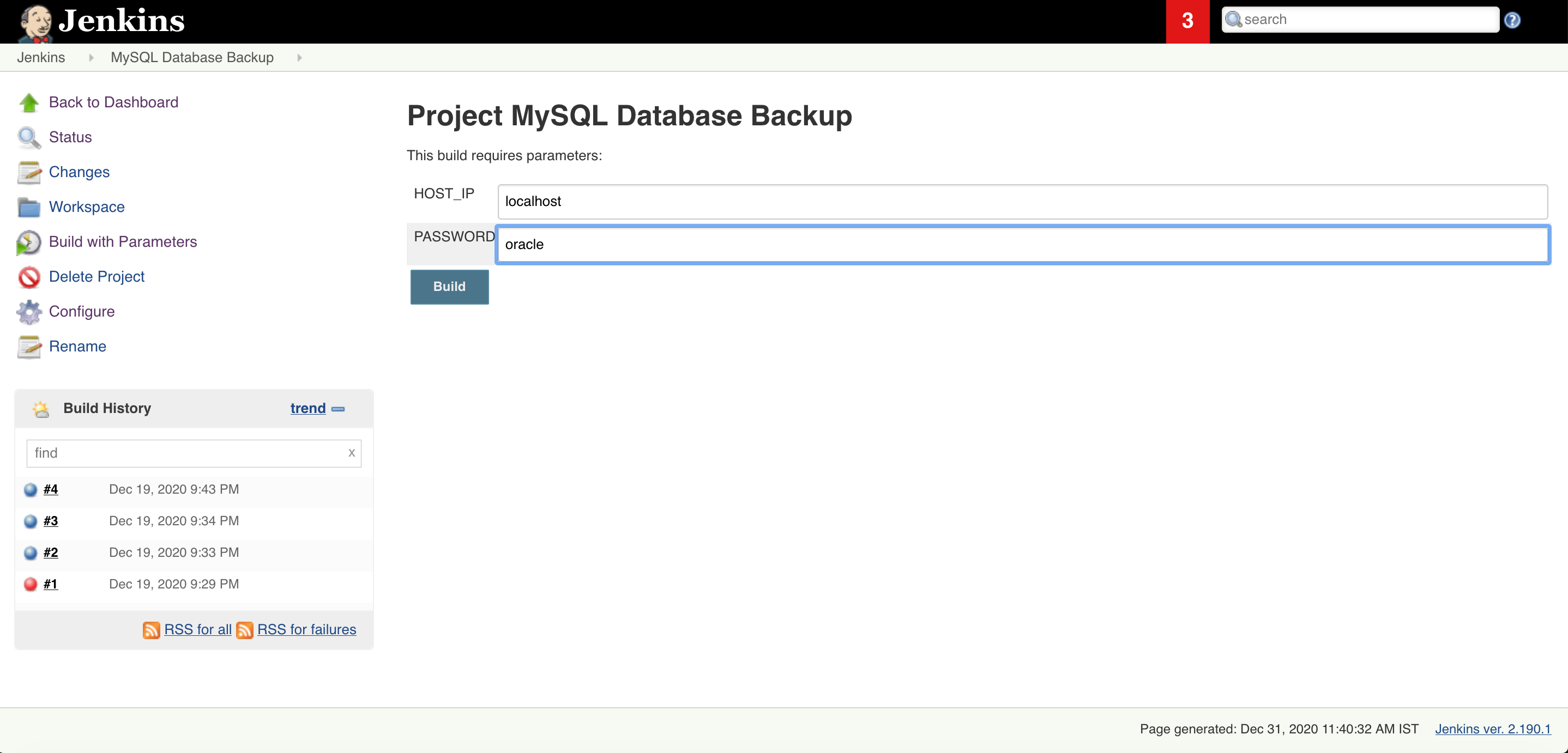
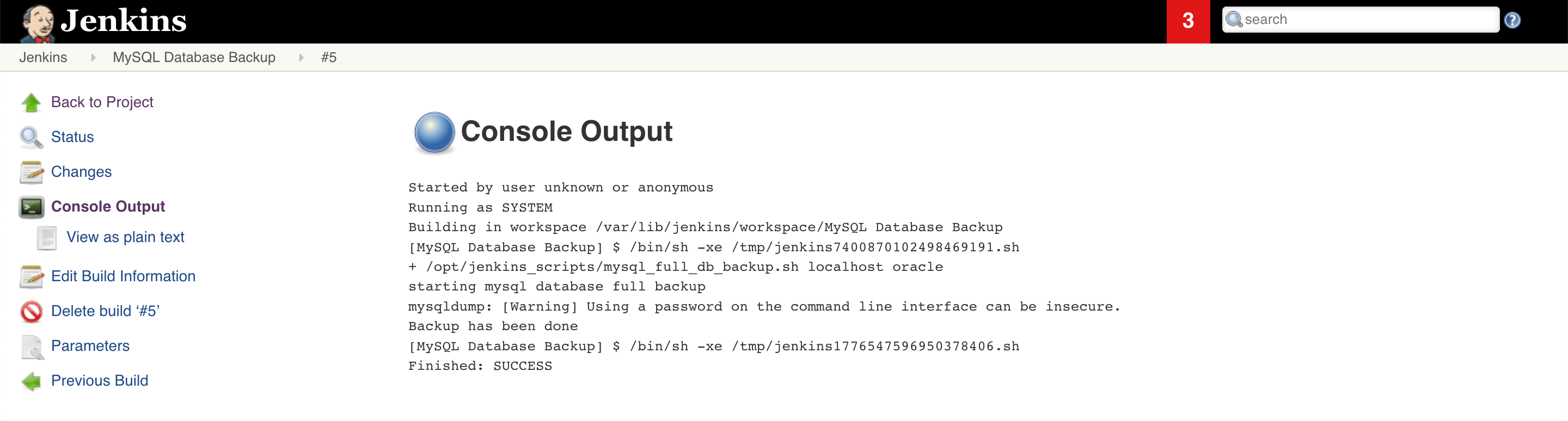
7.4 Once your job is executed go to that job open it in console output mode and check the status of the job. And you are DONE!!!
Read More
How to fix ORA-28368: cannot auto-create wallet
AWS Services and their Azure alternatives
How to Manage AWS S3 Bucket with AWS CLI
How to connect PostgreSQL Database from PgAdmin
How to create AWS rds PostgreSQL Database
Convert pem to ppk
How to Install PuTTy on Window
How to Install and create AWS EC2 Instance using Terraform
AWS MySQL RDS Database Creation using AWSCLI
How to Create MySQL Database with AWS RDS
How to connect to AWS MySQL / MariaDB RDS or EC2 database from MySQL WorkBench








